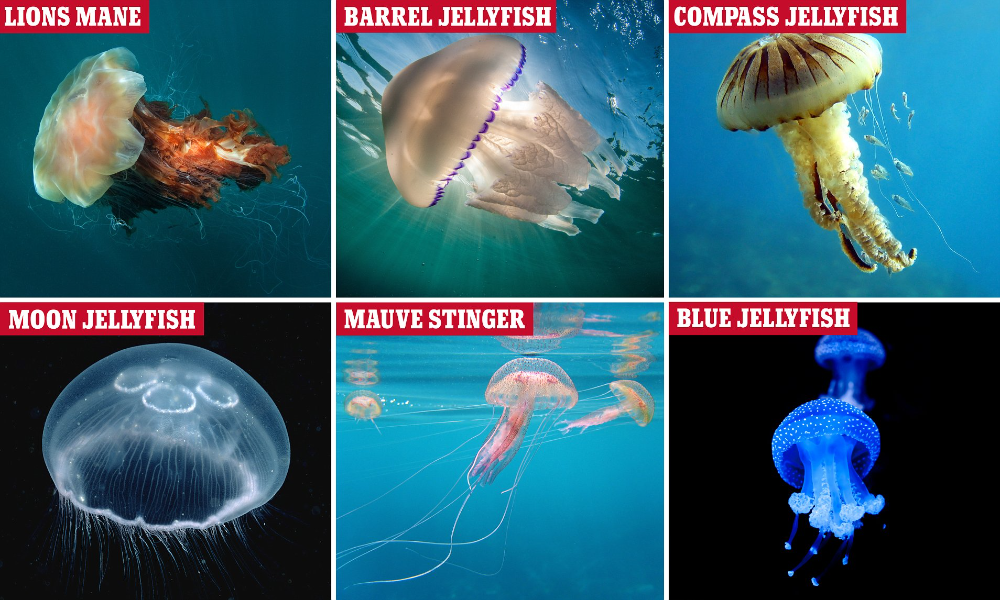
Have you ever wondered if jellyfish are aware of their own existence? It’s a fascinating question that has intrigued many researchers and animal lovers alike. Despite having no brains, jellyfish are highly adaptable creatures that have been around for over 500 million years. So, do they possess any level of consciousness or intelligence? In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of jellyfish and explore their cognitive abilities. Let’s find out if these mesmerizing creatures are capable of thinking, feeling, and perceiving their surroundings.

Do Jellyfish Possess Consciousness?
Jellyfish are fascinating creatures that have been the subject of many scientific studies. One of the questions that often come up is whether they are aware of their own existence. The answer to this question is no. Jellyfish do not have brains, which means that they do not possess the neural capacity necessary for consciousness. Therefore, jellyfish are not capable of being aware of their own existence.
The absence of a brain in jellyfish means that they lack the central processing unit that is necessary for consciousness. Without a brain, jellyfish do not have the ability to think, feel, or experience emotions. They are simply reactive animals that respond to stimuli in their environment.
It is important to note that just because jellyfish are not conscious does not mean that they are not alive. Jellyfish are multicellular organisms that are capable of carrying out a variety of biological processes. They can swim, reproduce, and respond to their environment in ways that are essential for their survival.
In conclusion, while jellyfish are not conscious and do not possess the ability to be aware of their own existence, they are still fascinating creatures that continue to intrigue scientists and laypeople alike. The absence of a brain does not diminish their importance or value in the ecosystem.
>> Must read What is SpongeBob schizophrenia?
The Cognitive Abilities of Jellyfish: An Exploration of their Intelligence
Jellyfish are fascinating creatures that have been around for more than 500 million years. Despite their long existence, they are very simple creatures with no brains, no bones, and no heart. Therefore, it is impossible for them to have an IQ since intelligence is a function of the brain.
Jellyfish belong to a group of animals known as cnidarians, which includes corals and sea anemones. These animals have a nervous system that is spread throughout their bodies, but they do not have a centralized brain. Instead, their behavior is controlled by a network of neurons that are distributed throughout their bodies.
Because they lack a brain, jellyfish do not have the ability to think, reason, or solve problems. They are purely instinctual creatures that simply respond to their environment. They can detect light, chemicals, and movement, which allows them to navigate and find food. However, they do not have the capacity for complex behaviors or learning.
In conclusion, jellyfish have no brains at all, so they do not even have an IQ. While they are capable of some basic responses to their environment, they cannot think or reason like more complex animals. Their simplicity is part of what makes them so intriguing, and studying them can provide valuable insights into the evolution of life on Earth.
Trending now – What mental illness does Dory have?
Exploring the Cognitive Abilities of Jellyfish.
Jellyfish are fascinating creatures that have been the subject of much discussion in regard to their cognitive abilities. However, the question remains: Can jellyfish think? The answer is no. It may come as a surprise to many, but jellyfish do not have a brain. They do possess a simple nervous system that runs along the base of their tentacles, which allows them to detect changes in their environment such as temperature, salinity, and touch. But this system is not complex enough to support cognitive processes such as thinking or decision making.
Since jellyfish lack a brain, they rely on automatic reflexes to respond to stimuli in their environment. For example, when a jellyfish’s tentacle brushes against an object, it will immediately withdraw its tentacle in response. The same goes for catching prey – it’s largely a matter of chance. Jellyfish simply drift along in the water, hoping that plankton or other small organisms will happen to bump into their tentacles.
In summary, while jellyfish are capable of responding to their environment, they do not possess the cognitive capabilities to think, reason, or make decisions. Their reliance on automatic reflexes is a testament to the incredible adaptability of these creatures in the absence of a central nervous system.

Unveiling the Smartest Animal on Earth: Which Species Reigns Supreme in Intelligence?
Chimpanzees are considered to be the most intelligent animals on the planet. They have the ability to manipulate their environment and surroundings to benefit themselves and their community. Chimpanzees have shown impressive problem-solving skills and can use tools to complete tasks efficiently. In fact, they have even outsmarted humans on several occasions. Studies have shown that chimpanzees are capable of understanding cause and effect, predicting outcomes, and using their intelligence to adapt to new situations. Their cognitive abilities are similar to those of a young human child, which allows them to learn from experience and develop new skills over time. In the animal kingdom, chimpanzees are undoubtedly the top contenders for the title of the most intelligent species.
Exploring the Possibility of Emotional Capability in Jellyfish
Jellyfish may not have emotions in the way we understand them, but they are not entirely devoid of any sensitivities. As mentioned, jellyfish have a complex neural network that allows them to respond to various stimuli in their environment. However, this response is purely instinctual and automatic, and not a result of any emotional experience.
Jellyfish do not have a brain, which is the organ responsible for processing emotions in most animals. Therefore, they cannot experience fear, happiness, or sadness in the same way that we do. However, studies have shown that jellyfish do have a rudimentary nervous system that allows them to respond to negative stimuli, such as predators or dangerous environments. They can detect changes in temperature, salinity, and even light, and use this information to move away from any threats.
It’s important to note that while jellyfish may not have emotions, they are still living organisms that deserve respect and care. We should strive to understand and appreciate these fascinating creatures for what they are, rather than projecting our human emotions onto them.
Which Pet Outsmarts the Rest? A Look into Animal Intelligence
When it comes to the pet with the highest IQ, dogs are the clear winner. According to the book “The Intelligence of Dogs,” which evaluates 131 dog breeds based on their intelligence, the border collie ranks as the most intelligent breed. These dogs have an impressive ability to understand and respond to complex commands and can learn new tasks quickly. In addition to their sharp intelligence, they are also known for their herding abilities and agility in various sports and competitions.
While dogs are widely regarded as one of the most intelligent pets, other animals have also showcased impressive cognitive abilities. For instance, some studies have suggested that certain species of primates, such as chimpanzees, orangutans, and gorillas, have shown remarkable cognitive abilities and can even learn sign language. However, when it comes to sheer intelligence, dogs remain at the top of the list.
Overall, while it is fascinating to explore the intelligence of different animals, it is important to remember that intelligence manifests in different ways across species. Each animal has unique cognitive abilities that have been shaped by their evolutionary history and environmental factors. As such, it is crucial to appreciate and respect the diverse ways in which animals interact with the world around them.
The Cognitive Abilities of Jellyfish: How Smart Are They?
Jellyfish, despite their fascinating and mesmerizing appearance, are not known to be intelligent creatures. As per marine biologist Stein Kaartvedt, jellyfish have a simple sensory system and do not possess a brain to process any information. This means that jellyfish do not have the ability to learn or remember things in the way that we do. They do not have the capacity for complex behavior or cognition.
Jellyfish are part of the phylum Cnidaria, which includes sea anemones and corals. They have a nerve net, which is a simple network of neurons that allows them to respond to their environment. However, this nerve net is not centralized like a brain, and it does not have the ability to process information in the same way that a brain does.
Despite their lack of intelligence, jellyfish have evolved some remarkable adaptations. For example, some species of jellyfish have the ability to bioluminesce, meaning they can produce light. This adaptation helps them to attract prey and mates in the dark depths of the ocean.
In conclusion, while jellyfish may be beautiful and fascinating creatures, they are not very intelligent. Their simple sensory organs and lack of a brain mean that they do not have the capacity for complex behavior or cognition. Nonetheless, their unique adaptations and important ecological roles make them a crucial part of our oceans’ ecosystems.
The Ability of Jellyfish to Perceive Humans.
Jellyfish are fascinating creatures that possess unique abilities. One of the most interesting features of jellyfish is their ability to sense changes in light and even see their surroundings to some extent. All jellyfish species have eye spots that give them this ability. These eye spots are usually located on the rim of their bells and are not the same as the eyes found in other animals.
While jellyfish eyes might not be as sophisticated as human eyes, some species have well-developed eye spots that allow them to see and hunt their prey. For example, the box jellyfish has complex eyes that are capable of forming images and detecting color. This makes them one of the few creatures in the world that have the ability to see in color.
However, it is important to note that not all jellyfish have well-developed eyes. Some species only have simple light-sensitive cells that can detect changes in light but cannot form images. Therefore, whether a jellyfish can see you or not depends on the species.
In conclusion, jellyfish have the ability to sense changes in light and some species have well-developed eye spots that give them the ability to see and hunt their prey. While not all jellyfish can see in the same way, it is remarkable that these creatures have evolved to have any visual capacity at all given their unique biology.
Brainless but Alive: The Fascinating Mystery of Jellyfish Existence
Jellyfish are certainly alive, even though they don’t have a centralized brain like humans or other animals. Instead, they possess a network of nerves called the “ring” nervous system, which is where their neurons are concentrated. This net of nerves acts as a processing station for sensory and motor activity in jellyfish. The neurons in this system send chemical signals to the muscles, allowing them to contract and swim through the water.
While jellyfish don’t have a brain, they do have a decentralized nervous system that enables them to perform basic functions such as movement and responding to stimuli. In fact, some scientists believe that jellyfish may be more complex than we previously thought, as they are able to respond to their environment and even make decisions without a traditional brain.
Despite not having a centralized brain, jellyfish are still very much alive and have adapted to their environment in fascinating ways. Their unique nervous system allows them to survive and thrive in the ocean, making them an important part of the marine ecosystem.
The Ability of Jellyfish to Perceive Humans: Do They Have Eyes on Us?
Jellyfish are commonly known for their gelatinous bodies and tentacles that can deliver painful stings to humans. However, not many people know that jellyfish can see, albeit not as clearly as humans. One particular species of jellyfish, Tripedalia cystophora, has eyes that allow it to see in a similar way to humans. These eyes are complex structures that contain a lens, a cornea, and a retina. Scientists have observed that the box jellyfish also uses its vision to locate habitats that it prefers and to hunt for prey. For instance, it can identify mangrove roots as a suitable place to hide or find food. Although jellyfish vision is not as sharp as human vision, it is still a significant ability that helps them survive in their aquatic environment.
Jellyfish may not possess consciousness or high intelligence levels like other animals, but they still hold a certain level of intrigue and fascination for scientists and nature enthusiasts. While they may not be sentient beings, the unique features and behaviors of jellyfish continue to amaze us and contribute to our understanding of the natural world.



